Remember when we all laughed at the idea of investing in digital coins with a dog’s face on them? Or when those intentionally ugly shoes were just a meme about terrible fashion?
The internet has developed a disturbing superpower: turning its most absurd jokes into tangible reality. What begins as satire in niche online forums somehow ends up reshaping economies, influencing major fashion houses, and even altering our language itself.
Let’s examine seven internet jokes that escaped their digital cages to roam free in our physical world—for better or significantly weirder.
1. Dogecoin => From Forum Joke to Financial Phenomenon#

In December 2013, two software engineers created Dogecoin as a direct parody of cryptocurrency speculation. It featured a Shiba Inu dog from a popular meme and was explicitly designed to mock the seriousness of Bitcoin. The joke came complete with Comic Sans font and intentionally broken English (“much wow,” “so currency”).
What happened next defies rational explanation.
The transformation from forum humor to financial instrument proceeded through several distinct phases:
The Irony Era
2013-2016
Early Dogecoin enthusiasts participated entirely through an ironic lens—they donated to bizarre causes (sponsoring a NASCAR driver, funding the Jamaican bobsled team) specifically because it seemed absurd. The humor came from treating something ridiculous with mock seriousness.The Celebrity Amplification
2019-2021
When Elon Musk and other high-profile figures began tweeting about Dogecoin, the joke expanded beyond its original context. New investors arrived who weren't in on the original joke—they simply saw something trending upward with famous endorsements.The Financial Reality Shift
2021-Present
As real money flowed in, financial institutions began offering Dogecoin trading, mainstream news covered its price movements, and the "joke" currency developed genuine economic consequences. The punchline had become a portfolio asset.
The line between irony and sincerity completely dissolved. Today, Dogecoin persists as both a self-referential joke and an actual store of value simultaneously—Schrödinger’s currency existing in two contradictory states at once.
2. Gorpcore => When Outdoor Fashion Became an Ironic Flex#
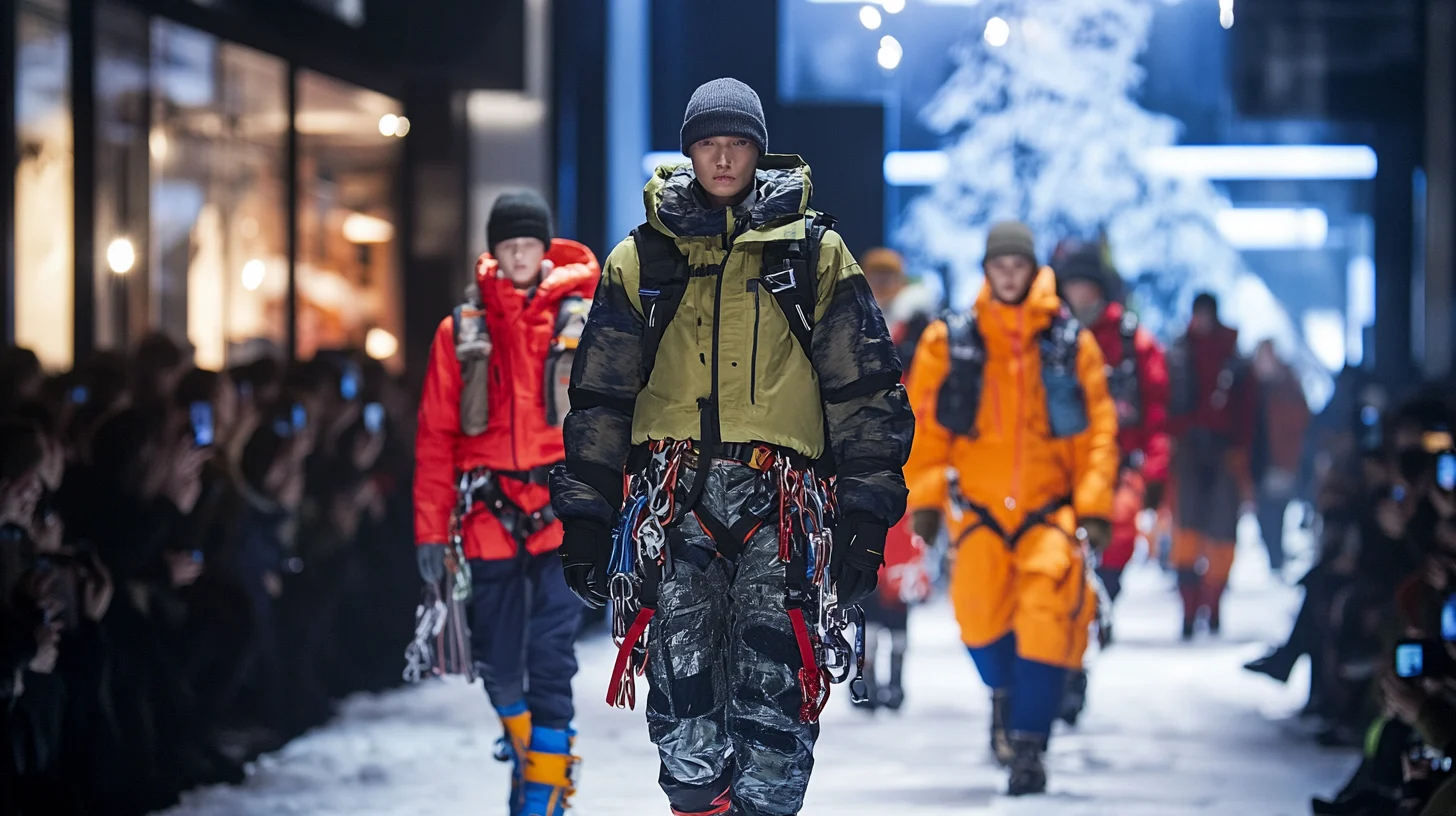

The term “gorp” originally referred to trail mix (“Good Old Raisins and Peanuts”) carried by serious hikers. Online fashion forums began using “gorpcore” around 2017 as a satirical descriptor for people wearing excessively technical outdoor gear in urban settings—an ironic jab at city dwellers sporting $700 Arc’teryx jackets to grab coffee while never venturing near actual mountains.
The joke focused on the absurd disconnect between these garments’ intended use (surviving extreme wilderness conditions) and their deployment (protecting against mild drizzle during a three-block walk).
What was once mockery morphed into genuine fashion movement—high-end designers like Balenciaga and Gucci began creating their own aggressively utilitarian pieces. Fashion magazines promoted “performance wear” as the new luxury. The North Face collaborated with Gucci on a collection featuring $1,400 hiking boots destined never to touch dirt.
Today, gorpcore has become so established that many of its current enthusiasts have no idea it began as a joke about performative practicality. The outdoor brands being satirized have fully embraced their unexpected fashion status, creating urban-focused lines with technical features no city dweller could possibly need.
The transformation completed when outdoor forums began complaining that actual hikers could no longer afford essential gear because prices had skyrocketed due to fashion demand—the joke had reversed direction entirely.
3. “OK Boomer” => From Dismissive Meme to Generational Warfare#
What began in 2019 as a flippant comeback on TikTok rapidly evolved into something much larger. Gen Z users initially deployed “OK Boomer” as a humorous way to dismiss perceived out-of-touch opinions, usually accompanied by eye-rolling or dismissive hand gestures.
The phrase operated as light mockery until it underwent a remarkable metamorphosis:
The transformation accelerated when New Zealand MP Chlöe Swarbrick used the phrase in parliament after being heckled during a climate change speech. Within months, the phrase appeared in:
- Multiple trademark applications (over 20 companies filed for ownership)
- Congressional hearings (referenced during testimony)
- Supreme Court deliberations (mentioned in age discrimination case discussions)
- Academic sociology papers analyzing intergenerational conflict
- HR policy updates at major corporations addressing ageism concerns
What makes this case study particularly fascinating is how a phrase intended as a throwaway joke became serious enough to trigger genuine intergenerational tension, policy discussions, and academic analysis. The joke didn’t just escape the internet—it altered real-world discourse about age, authority, and social power.
4. Ugly Sneakers => When Hideous Became High Fashion#
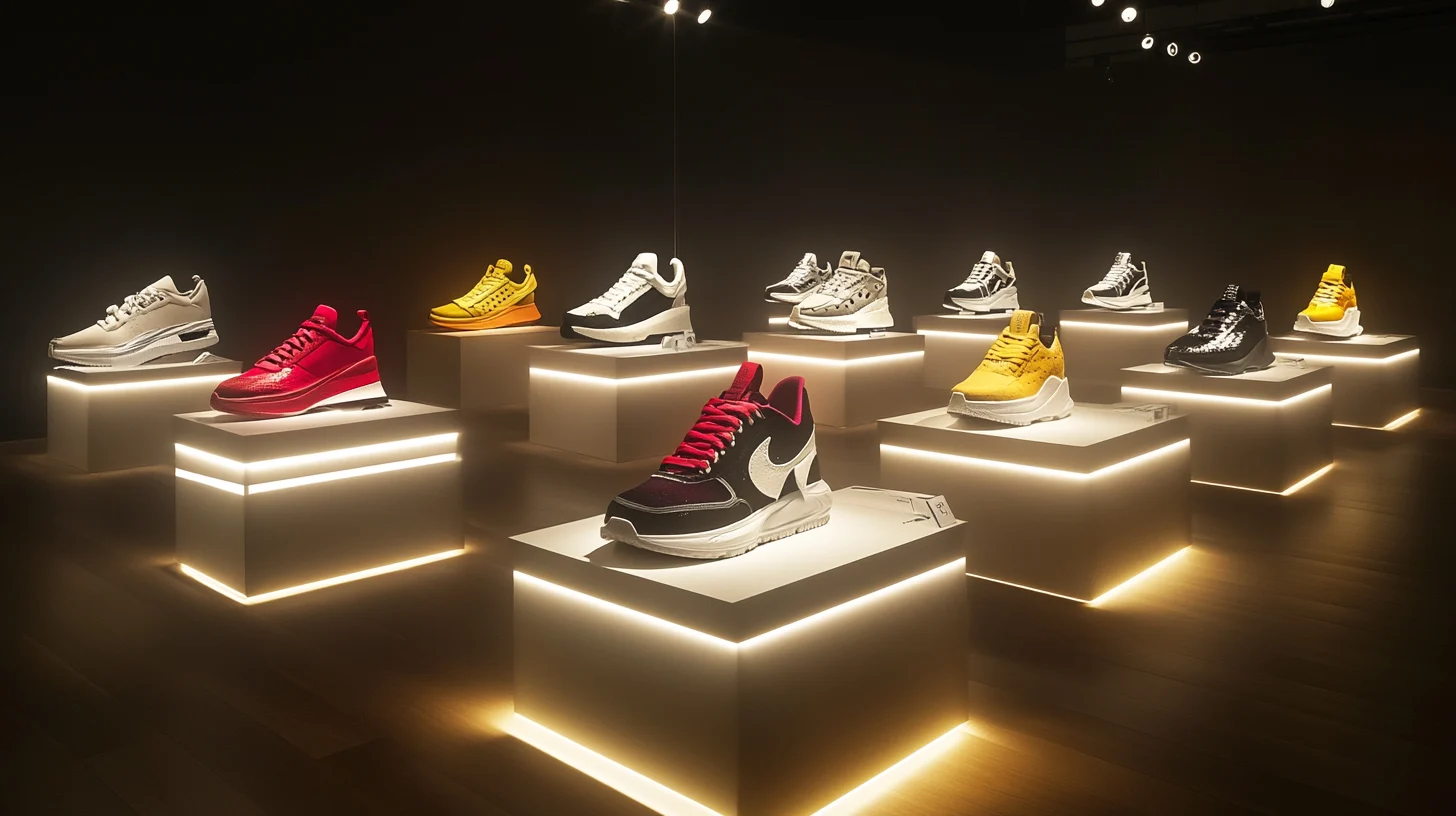

Around 2017, internet fashion forums began sharing images of deliberately hideous chunky sneakers as a form of aesthetic shitposting. The joke centered on creating shoes so aggressively unattractive they could only be worn ironically—massive platforms, chaotic color schemes, and proportions that defied conventional design principles.
What happened next surprised everyone involved in the original joke:
- Balenciaga released the Triple S sneaker—a shoe so cartoonishly large and visually busy it appeared to be directly inspired by the meme
- Fashion influencers began wearing these “ugly” shoes unironically
- The $1,000+ price tags created a status paradox where the ugliness became a feature signaling insider knowledge
- Traditional athletic brands began creating their own “ugly” designs to capture market share
- The trend spread from sneakers to all footwear, launching the “dad shoe” aesthetic
This trend represents a perfect example of what cultural theorists call “irony collapse”—the point at which something embraced ironically becomes embraced sincerely, with the original joke context completely forgotten. Many consumers purchasing chunky designer sneakers today have no awareness they’re participating in what began as a visual punchline.
The “ugly sneaker” phenomenon also demonstrates how the internet accelerates fashion cycles—what would have taken decades to evolve through traditional trend mechanisms occurred in less than three years.
5. “Bird Aren’t Real” => When Satire Becomes Indistinguishable From Conspiracy#
In 2017, college student Peter McIndoe spontaneously created the “Birds Aren’t Real” movement as an absurdist parody of conspiracy culture. The joke claimed that the U.S. government had replaced all birds with surveillance drones between 1959 and 2001.
The satire included deliberately ridiculous elements:
- Birds sit on power lines to “recharge”
- Bird droppings are “tracking devices”
- The “Birds Aren’t Real” movement had been fighting this “truth” since the 1970s
McIndoe created the joke to mock how easily conspiracy theories spread online. The movement used all the familiar conspiracy theory hallmarks—urgent tone, claimed insider knowledge, selective “evidence,” and calls to “wake up”—but applied to an obviously false premise.
What started as a clear joke underwent a fascinating transformation:
- The movement gained actual believers who didn’t recognize the satire
- Merchandise sales (t-shirts, stickers) exploded as both ironic and sincere purchases
- Real protests formed with participants holding “Birds Aren’t Real” signs
- Media began covering it as a genuine cultural phenomenon
- The movement’s founder eventually appeared on national television to explain the satire
What makes this case unique is how the joke morphed into a meta-social experiment about misinformation itself. The movement now exists as a deliberate parody that simultaneously:
- Mocks conspiracy thinking
- Creates community through shared inside jokes
- Demonstrates how easily misinformation spreads
- Confuses observers unable to distinguish satire from sincerity
This “joke” has been referenced in academic papers about post-truth media environments and now appears in college courses on misinformation—a satirical meme transformed into a serious educational tool about the nature of online belief systems.
6. Cottagecore => From Ironic Escapism to Actual Lifestyle Movement#
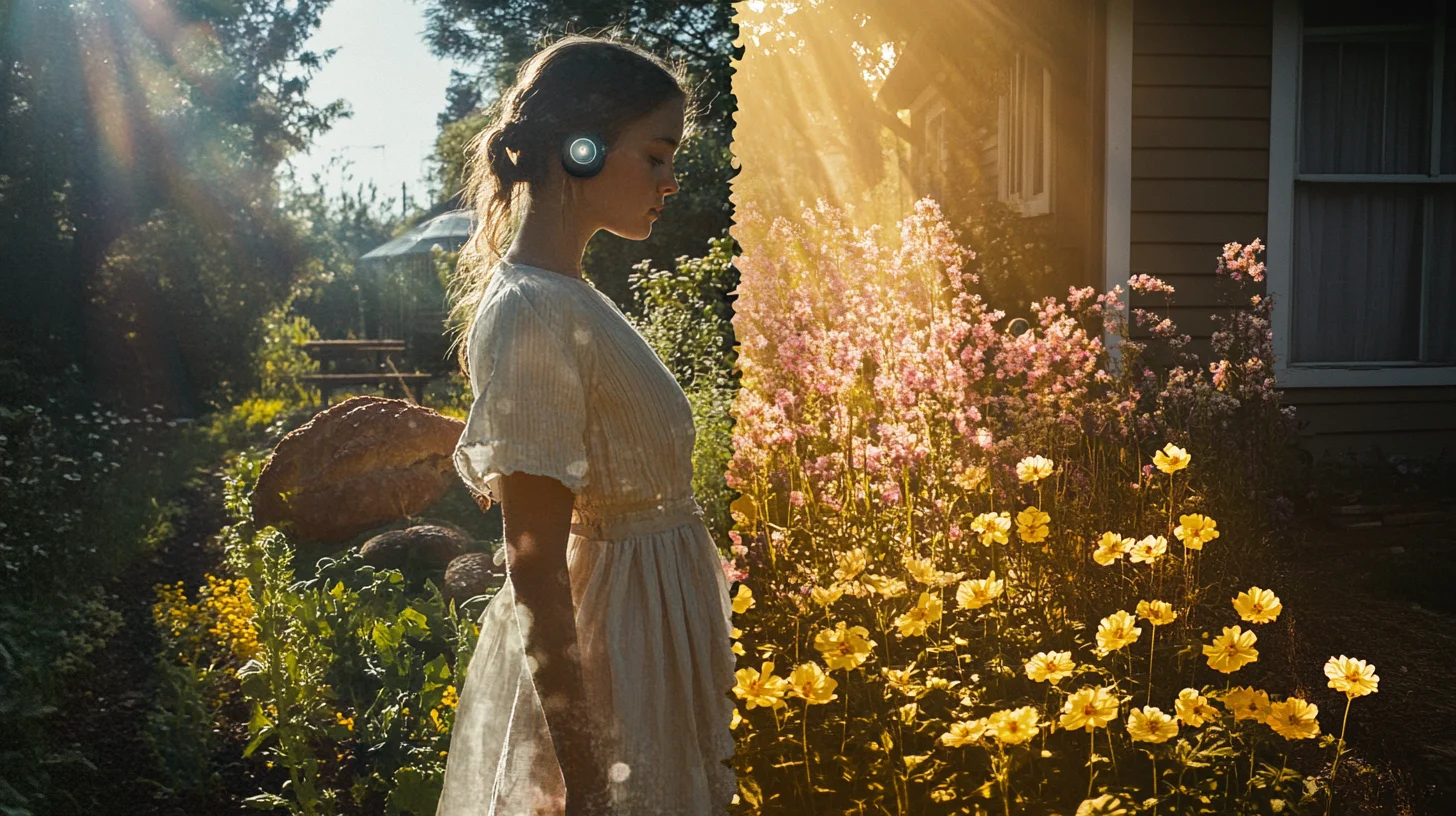

Around 2018, Tumblr and later TikTok users began sharing images of an idealized rural existence they dubbed “cottagecore”—a deliberately romanticized vision of agricultural life featuring flowing dresses, homemade bread, flower gardens, and rustic interiors.
The aesthetic initially functioned as a fantasy escape from modern urbanism and technology dependence, often shared with a wink of irony about its unrealistic portrayal of rural life (conspicuously absent: actual farming hardships, isolation, physical labor).
The transformation from online aesthetic to lifestyle choice proceeded through these phases:
The Aesthetic Phase
2018-2020
Image collections, mood boards, and stylized photography focused on visual elements without actionable lifestyle components. The trend existed primarily as a fantasy escape valve during early pandemic lockdowns.The Craft Revival
2020-2021
Followers began learning actual traditional skills—bread baking, sewing, herb gardening, candle making—as pandemic restrictions limited outside activities. What began as aesthetic appreciation became skill acquisition.The Physical Relocation
2021-Present
A measurable demographic shift occurred as young adults began moving to rural areas explicitly citing "cottagecore" as inspiration. Real estate agents reported showing properties to clients specifically requesting "cottagecore-friendly" homes with gardens and historical features.
Today, cottagecore has generated measurable economic impacts:
- Rural property value increases in Instagram-photogenic areas
- Revival of traditional craft supplies and equipment sales
- Fashion lines explicitly marketed as “cottagecore attire”
- Interior design services specializing in the aesthetic
- Cooking classes teaching “cottagecore cuisine”
What began as a half-ironic internet aesthetic has contributed to actual demographic shifts, with Gen Z and Millennials migrating to rural communities in patterns that differ from previous generational trends—the fantasy has become actual relocation decisions.
7. “Moving to Canada” => From Election Cycle Joke to Expatriate Reality#
For decades, Americans have joked about “moving to Canada” if their preferred candidate loses a presidential election. This threat became a recurring meme during each election cycle, treated as obvious hyperbole by both those making the statements and those hearing them.
Data shows that few people historically followed through—the joke functioned as emotional venting rather than actual relocation planning.
However, something changed after 2016:
The exponential increase in Americans actually relocating to Canada represents one of the most literal examples of an internet joke materializing into concrete action. Canadian immigration attorneys report clients specifically citing political memes and social media discussions as initial inspiration for what became serious relocation plans.
What makes this transformation particularly noteworthy:
- The meme existed for multiple decades as pure hyperbole before manifesting in behavior change
- The action requires enormous life disruption unlike purchasing decisions or aesthetic choices
- The trend continues increasing rather than following normal meme decay patterns
- The joke has now become a self-fulfilling prophecy with real demographic consequences
Canadian government offices now specifically prepare for application surges following U.S. election cycles, and multiple Canadian provinces have created recruiting programs explicitly targeting Americans expressing political dissatisfaction online.
The joke has become so literal that immigration sites now crash on U.S. election nights—digital infrastructure buckling under the weight of what was once merely a rhetorical device.
The Meme-to-Reality Pipeline#
What these seven examples reveal is a consistent pattern in how internet jokes transform into tangible reality:
This pattern accelerates through several key mechanisms:
1. Context Collapse#
As jokes spread beyond their original communities, the ironic framing disappears. New audiences encounter the content without understanding it began as satire, creating serious engagement with what was intended as mockery.
2. Commercial Exploitation#
Businesses rapidly identify and monetize viral content regardless of its original intent. This commercial legitimization transforms jokes into products, services, and marketing campaigns that further obscure the satirical origins.
3. Identity Signaling#
What begins as ironic participation quickly transforms into genuine identity markers as people incorporate trending elements into their self-expression—the joke becomes part of who they are rather than something they’re mocking.
4. Media Amplification Cycles#
Traditional media coverage of internet phenomena typically strips away nuance, presenting jokes as sincere movements and further accelerating their transition from irony to earnestness.
5. Institutional Adaptation#
When enough people treat a joke as real, institutions must respond as if it were real—creating policies, products, and infrastructure that permanently cement the transformation.
The Blurring of Digital and Physical Realities#
The seven trends examined here suggest several profound implications:
The accelerating timeline between joke creation and real-world manifestation (what once took decades now occurs in months)
The increasing scale of joke-to-reality transformation (affecting economic markets, demographics, and global commerce)
The diminishing ability to distinguish between sincere movements and elaborate satire
The commercial infrastructure that now exists specifically to monetize irony-to-sincerity pipelines
As one internet philosopher noted: “The problem isn’t that we can’t tell what’s a joke anymore. The problem is that jokes themselves have become a legitimate pathway to reality.”
Is Everything Eventually Real?#
Perhaps the most unsettling implication is what these examples suggest about the future. If internet jokes reliably transform into reality, what current memes might be previewing our actual future?
Some possibilities currently in the “just joking” phase that show early signs of reality transition:
- Digital land ownership in non-existent “metaverse” properties
- AI companions replacing human relationships
- Voluntary technological implants for non-medical purposes
- Aesthetic-based dietary restrictions detached from health considerations
- Corporate personhood taken to extremes of emotional attachment
The next time you laugh at an absurd internet joke, consider this: you might be glimpsing your actual future. Today’s ironic shitpost has a disturbing tendency to become tomorrow’s sincere lifestyle, commercial product, or social movement.
The boundary between digital joke and physical reality has become so permeable that perhaps we should start taking internet humor more seriously—because the world certainly does.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do some internet jokes become reality while others fade away?
Is this phenomenon new or just more visible now?
Should we be concerned about jokes becoming reality?
Who benefits from this joke-to-reality pipeline?
Can this process be intentionally triggered or manipulated?
As the line between digital humor and physical reality continues to blur, perhaps the most important question isn’t whether a trend began as a joke, but whether we’re comfortable with the world these materialized jokes are creating.
